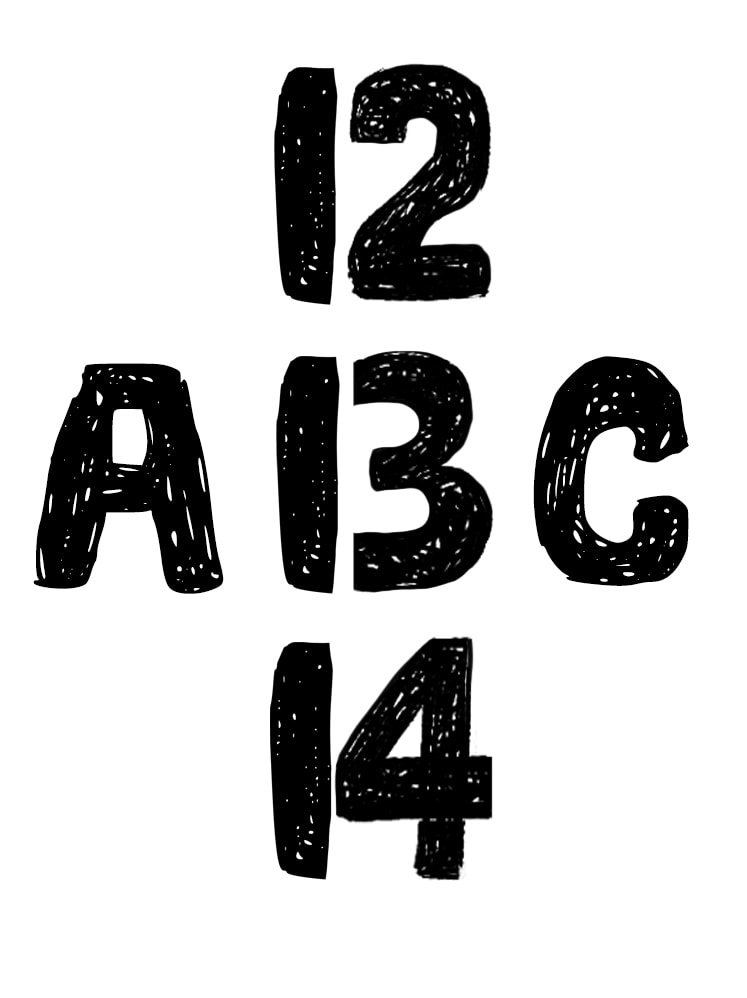Infusing Stable Diffusion (Image to Image generation)
Infusing Stable Diffusion 💉
An Image Generation approach to add baisses from prior images \
Stable Diffusion is a recent text-to-image latent diffusion model created by the researchers and engineers from CompVis, Stability AI and LAION. It’s trained on 512x512 images from a subset of the LAION-5B database. It has become widely popularized as Huggingaface has made it readily available throughd the 🤗 Hugging Face 🧨 Diffusers library.
There exist some prior approaches for generating images from prior images such as Img2Img, where the biasing image is used as the initial image and denoised with stable diffusion to match the text prompt. We propose an alternative approach to Img2Img generation where Stable diffusion is initialized normally (with noisy latents), and the biasing images are fed into the model to biass the denoising steps to incorporate the biassing images. We call this approach Infusion as concepts are infused into the model.
The Approach
Briefly, here is what occurs in the Infusion approach.
A biasing image is passed through the Stable Diffusion Pipeline. That is, it is encoded into the latent space, and fed as input into the Denoising U-Net along with the current image. Within the U-Net, the features (scaled) of the biassing image are extracted and added to the features of the image currently being generated. This causes the output of the U-Net to be biassed by the image, and the denoising step becomes effected by the biassing image. This effect of the biasing image starts to appear in the result.
Multiple biasing images can be sent into U-Net, averaging their extracted features is expected to capture higher level concepts.
Motivation
This approach can help better understand what is occuring in the Stable Diffusion Model. The approach adds biasses at different layers of the U-Net, and by changing the weights of at the different layers, it can expose the the information that is provided at the different layers of the U-Net. Experimentation with the model weights gives insight into the interaction between the different layers of the U-Net, including the residual layers. Lastly, this method sheds light on the nature of the denoising process as a process that (a) detects features in the current image, and (b) makes them better defined.
(Engineering Motivation) In Stable Diffusion & the Img2Img approach, the model (U-Net specifically) uses the features that exist in the image to denoise them, and make them more realistic. That is, if there is a green circle with some noise, the Diffusion approach will remove this noise leaving only the green circle. The Infusion 💉 approach moves this process into the U-Net Model itself. It adds features of the biasing Image to the current features within the U-Net Model. This has the effect of recognizing features from the biasing image itself, and denoising them into existence. That is, the process generates the biasing image rather than starting with the initial image. View the following image as an example.
(Psychology Motivation) In psychology/neuroscience there is a concept of top down processing where thinking of something influences what we precieve. For example, in the following image, looking at the middle character, it transforms between the letter ‘B’ and the number ‘13’ depending on whether we focus on ‘ABC’ or ‘12 13 14’. Infusion aims to act as a similar approach in that adding features (thinking about a concept) from a biasing image, causes it to appear in the generated image.